Data Units
Inhaltsverzeichnis
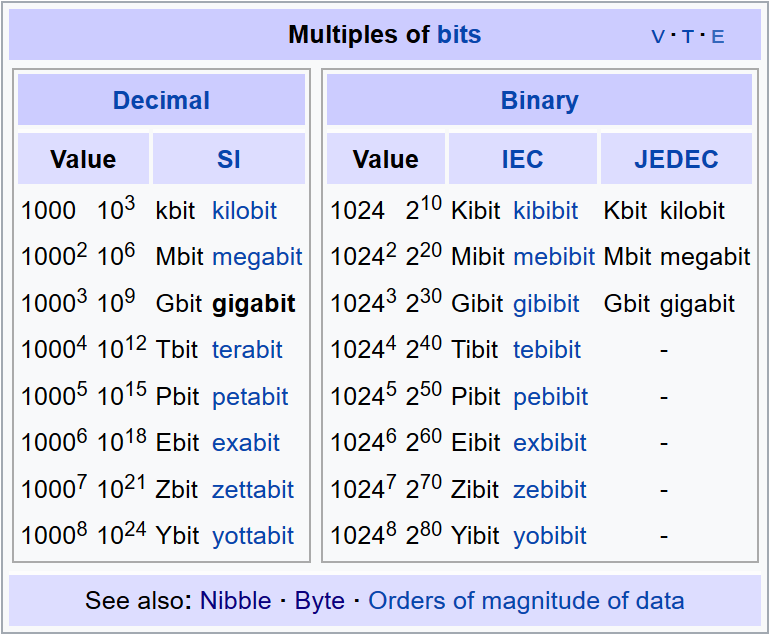
[Verbergen]Bits
Example:
1 Gbit = 1'000'000'000 bit
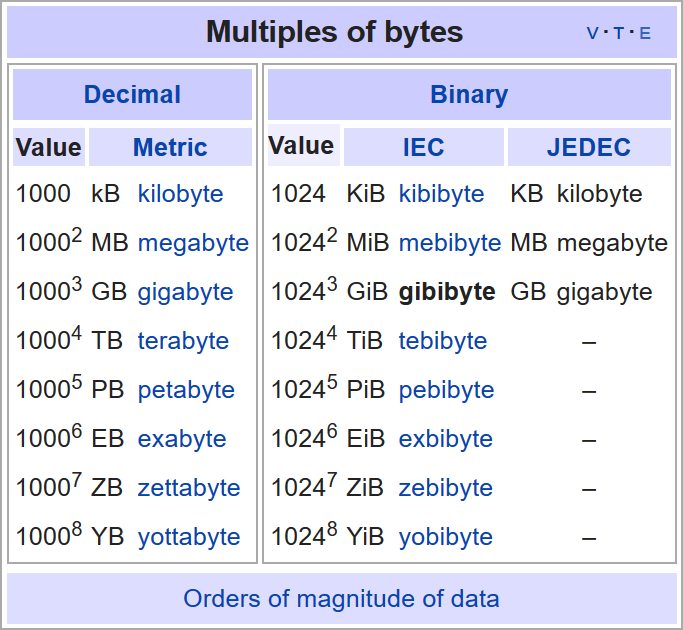
Bytes
Example:
1 GB = 1'000'000'000 Bytes
1 GiB = 1'073'741'824 Bytes
Definitions of 1 KB
1000 Bytes
In the International System of Units (SI) the prefix kilo means 1000; therefore, one kilobyte is 1000 bytes. The unit symbol is kB.
This is the definition recommended by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). This definition, and the related definitions of the prefixes mega (1000000), giga (1000000000), etc., are most commonly used for data transfer rates in computer networks, internal bus, hard drive and flash media transfer speeds, and for the capacities of most storage media, particularly hard drives,[3] flash-based storage,[4] and DVDs. It is also consistent with the other uses of the SI prefixes in computing, such as CPU clock speeds or measures of performance.
The IEC 80000-13 standard uses the term 'byte' to mean eight bits (1 B = 8 bit). Therefore, 1 kB = 8000 bit. One thousand kilobytes (1000 kB) is equal to one megabyte (1 MB), where 1 MB is one million bytes.
1024 Bytes
The kilobyte has traditionally been used to refer to 1024 bytes, a usage still common. The usage of the metric prefix kilo for binary multiples arose as a convenience, because 1000 approximates 1024.
The binary interpretation of metric prefixes is still prominently used by the Microsoft Windows operating system, which is used on 90% of the world's personal computers. They are also used for random-access memory capacities, such as main memory and CPU cache sizes, due to the binary addressing of memory.
The binary representation of 1024 bytes typically uses the symbol KB, with an uppercase letter K. The B is often omitted in informal use. For example, a processor with 65,536 bytes of cache memory might be said to have "64K" of cache. In this convention, one thousand and twenty-four kilobytes (1024 KB) is equal to one megabyte (1 MB), where 1 MB is 10242 bytes.
Quelle: