InfluxDB 2.x: Task: Downsampling: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Admin (Diskussion | Beiträge) K |
Admin (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| + | [[Datei:00-influxdb downsampling.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | |||
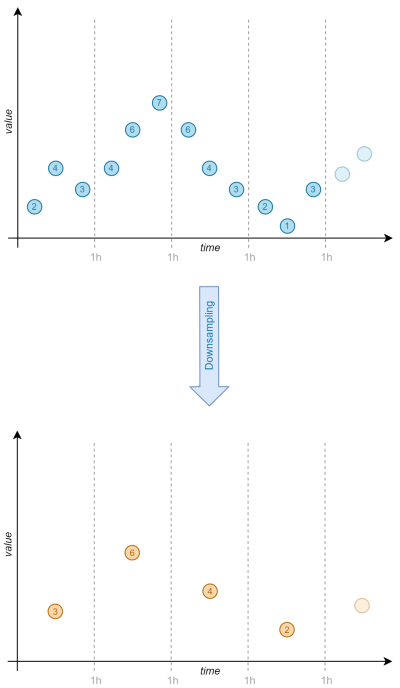
| + | The following downsampling examples calculates the '''mean value (for an one hour window) of every series and writes in a new Influx Database''' respectively Influx bucket. | ||
| + | |||
== Flux (Tasks) - InfluxDB 2.x == | == Flux (Tasks) - InfluxDB 2.x == | ||
''Flux is InfluxData’s functional data scripting language designed for querying, analyzing, and acting on data. Beginning with InfluxDB 1.8.0, Flux is available for production use along side InfluxQL.'' | ''Flux is InfluxData’s functional data scripting language designed for querying, analyzing, and acting on data. Beginning with InfluxDB 1.8.0, Flux is available for production use along side InfluxQL.'' | ||
| − | + | <pre> | |
| + | option task = {name: "<TASK_NAME>", every: 1h} | ||
| + | |||
| + | data = from(bucket: "<SOURCE_BUCKET>") | ||
| + | |> range(start: -duration(v: int(v: task.every) * 2)) | ||
| + | |> filter(fn: (r) => | ||
| + | (r._measurement =~ /.*/)) | ||
| + | |||
| + | data | ||
| + | |> aggregateWindow(fn: mean, every: 1h) | ||
| + | |> filter(fn: (r) => | ||
| + | (exists r._value)) | ||
| + | |> to(bucket: "<DESTINATION_BUCKET>", org: "<YOUR_INFLUX_ORGANISATION>") | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| Zeile 12: | Zeile 29: | ||
== InfluxQL - InfluxDB 1.x == | == InfluxQL - InfluxDB 1.x == | ||
''InfluxQL is an SQL-like query language for interacting with InfluxDB. It has been crafted to feel familiar to those coming from other SQL or SQL-like environments while also providing features specific to storing and analyzing time series data. However InfluxQL is not SQL and lacks support for more advanced operations like UNION, JOIN and HAVING that SQL power-users are accustomed to. This functionality is available with Flux.'' | ''InfluxQL is an SQL-like query language for interacting with InfluxDB. It has been crafted to feel familiar to those coming from other SQL or SQL-like environments while also providing features specific to storing and analyzing time series data. However InfluxQL is not SQL and lacks support for more advanced operations like UNION, JOIN and HAVING that SQL power-users are accustomed to. This functionality is available with Flux.'' | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | CREATE CONTINUOUS QUERY <CONTINUOUS_QUERY_NAME> ON <INFLUXDB_NAME> BEGIN SELECT mean(*) INTO <INFLUXDB_NAME>.<DESTINATION_RETENTION_POLICY_NAME>.:MEASUREMENT FROM <SOURCE_INFLUXDB_NAME>.<SOURCE_RETENTION_POLICY_NAME>./.*/ GROUP BY time(1h), * END | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
Version vom 14. Dezember 2020, 15:13 Uhr
The following downsampling examples calculates the mean value (for an one hour window) of every series and writes in a new Influx Database respectively Influx bucket.
Flux (Tasks) - InfluxDB 2.x
Flux is InfluxData’s functional data scripting language designed for querying, analyzing, and acting on data. Beginning with InfluxDB 1.8.0, Flux is available for production use along side InfluxQL.
option task = {name: "<TASK_NAME>", every: 1h}
data = from(bucket: "<SOURCE_BUCKET>")
|> range(start: -duration(v: int(v: task.every) * 2))
|> filter(fn: (r) =>
(r._measurement =~ /.*/))
data
|> aggregateWindow(fn: mean, every: 1h)
|> filter(fn: (r) =>
(exists r._value))
|> to(bucket: "<DESTINATION_BUCKET>", org: "<YOUR_INFLUX_ORGANISATION>")
More information's about "Flux Tasks": https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v2.0/process-data/common-tasks/downsample-data/#example-downsampling-task-script
InfluxQL - InfluxDB 1.x
InfluxQL is an SQL-like query language for interacting with InfluxDB. It has been crafted to feel familiar to those coming from other SQL or SQL-like environments while also providing features specific to storing and analyzing time series data. However InfluxQL is not SQL and lacks support for more advanced operations like UNION, JOIN and HAVING that SQL power-users are accustomed to. This functionality is available with Flux.
CREATE CONTINUOUS QUERY <CONTINUOUS_QUERY_NAME> ON <INFLUXDB_NAME> BEGIN SELECT mean(*) INTO <INFLUXDB_NAME>.<DESTINATION_RETENTION_POLICY_NAME>.:MEASUREMENT FROM <SOURCE_INFLUXDB_NAME>.<SOURCE_RETENTION_POLICY_NAME>./.*/ GROUP BY time(1h), * END
More information's about "Continuous Queries": https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v1.8/query_language/continuous_queries/
Example calculation of total Metric-points per bucket
For example we are writting 200 Metric-points per second, this means:
- ~ 12'000 Metric-points per minute
- ~ 720'000 Metric-points per hour
- ~ 17'000'000 Metric-points per day
- ~ 518'000'000 Metric-points per month
Assumption we have following Buckets (Influx databases):

red = number of Metric-points, green = number of series, blue = total Metric-points